APEX_AUTOMATION is a shared component feature that helps developers automate activities and tasks. It can trigger itself automatically at a specific time and event. These events could be yearly, monthly, hourly or weekly. These activities could be like sending emails, auditing tables processing orders etc. APEX_AUTOMATION can execute multiple processes sequentially.
Few sample activities
Processing Orders
Auto-approving requests
Sending email alerts
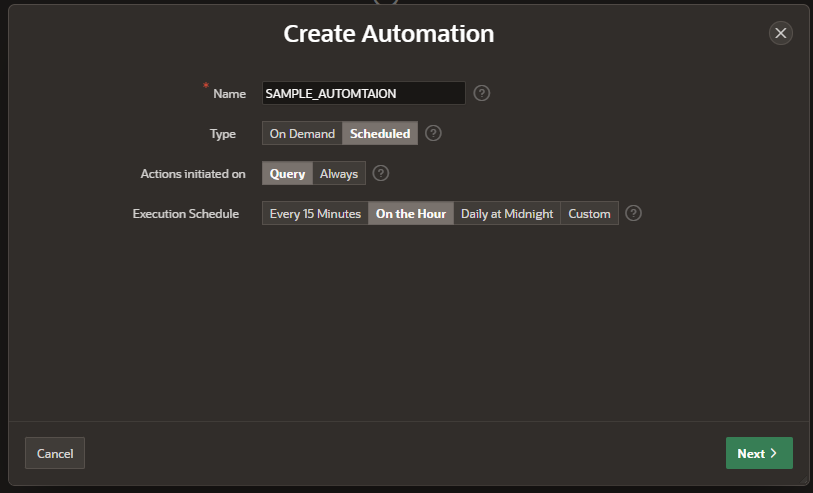
Steps to create the APEX_AUTOMTAION.
Go to Shared components
Go to Workflows and Automations
Click on Automations
Click on Create
Configurations
Name: Name of automation
Static ID: Static ID for this automation. The static ID is used when manually executing the automation with the APEX_AUTOMATION package (APEX_AUTOMATION.EXECUTE)
Type:
On-Demand: Can be executed on specific demand
Scheduled: Time event (Weekly, Daily, Hourly and Minutely)
Actions: List of actions which will be executed
Additional Code Execution:
Initialization Procedure: Provide the name of an Initialization Procedure, which is either defined as a PL/SQL object in the database schema, or in the above Executable Code. APEX will execute that procedure at the very beginning of an automation execution.
Before Row Processing Procedure: Provide the name of a Before Row Processing Procedure, which is either defined as a PL/SQL object in the database schema, or in the Executable Code. APEX will execute that procedure for each row, before it starts executing the defined actions.
View Documentation
Cleanup Procedure: Provide the name of a Cleanup Procedure, which is either defined as a PL/SQL object in the database schema, or in the Executable Code. APEX will execute that procedure at the very end of the automation execution.
Let’s take the example code for action, it will send an email.
— Example One: Plain Text only message
DECLARE
l_body CLOB;
l_id NUMBER;
BEGIN
l_body := ‘Thank you for your interest in the APEX_MAIL
package.’||utl_tcp.crlf||utl_tcp.crlf;
l_body := l_body ||’ Sincerely,’||utl_tcp.crlf;
l_body := l_body ||’ The Application Express Dev Team’||utl_tcp.crlf;
l_id := apex_mail.send(
p_to => ‘some_user@somewhere.com’, — change to your email address
p_from => ‘some_sender@somewhere.com’, — change to a real senders email address
p_body => l_body,
p_subj => ‘APEX_MAIL Package – Plain Text message’);
END;
/
After running the automation we can see the email sent
APEX views to create the console history
APEX_APPL_AUTOMATIONS: Stores the meta data for automations of an application.
APEX_APPL_AUTOMATION_ACTIONS: Identifies actions associated with an automation APEX_APPLICATIONS
APEX_AUTOMATION_LOG : Log of automation executions. APEX_APPL_AUTOMATIONS
APEX_AUTOMATION_MSG_LOG: Messages of an automation execution.
Below reports can show the details about the automation, in the log we can see the successful Execution no.
Now let’s try Operating automation with API.
APEX_AUTOMATION package API has multiple procedures and functions to operate the automation.
DISABLE Procedure
ENABLE Procedure
EXECUTE Procedure
EXECUTE for Query Context Procedure
EXIT Procedure
GET_LAST_RUN Return Function
GET_LAST_RUN_TIMESTAMP Function
LOG_ERROR Procedure
LOG_INFO Procedure
LOG_WARN Procedure
RESCHEDULE Procedure
SKIP_CURRENT_ROW Procedure
Let’s have a sample table to test APEX_AUTOMATION functions and procedures. Create a table as TEST_AUTOMATION
Create table test_automation
(
ID NUMBER GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
CODE varchar2(100),
exec_time date
);
Create New AUTOMATION to work on.
Name: ONTOOR_AUTOMATION
Static ID: ontoor-automation
Run and see if the AUTOMATION is working fine.
DECLARE
l_filters apex_exec.t_filters;
BEGIN
— apex_session.create_session( 94553, 1, ‘DEMO’ ); — If not executing from APEX
apex_automation.execute(
p_application_id => 94553,
p_static_id => ‘sample-automation’,
p_filters => l_filters );
END;
AUTOMATION filters
Automation filters are used as Predicate on Automation query, It applies a filter to the automation query on the column selected. The below code applies a filter to the automation query on the DEPTNO column (DEPTNO = 10).
DECLARE
l_filters apex_exec.t_filters;
BEGIN
— apex_session.create_session( 94553, 1, ‘DEMO’ ); — If not executing from APEX
apex_exec.add_filter(
p_filters => l_filters,
p_column_name => ‘DEPTNO’,
p_filter_type => apex_exec.c_filter_eq,
p_value => 10 );
apex_automation.execute(
p_application_id => 94553,
p_static_id => ‘sample-automation’,
p_filters => l_filters );
END;
…… In progress
The post APEX_AUTOMATION in oracle APEX appeared first on Ontoor blogs.